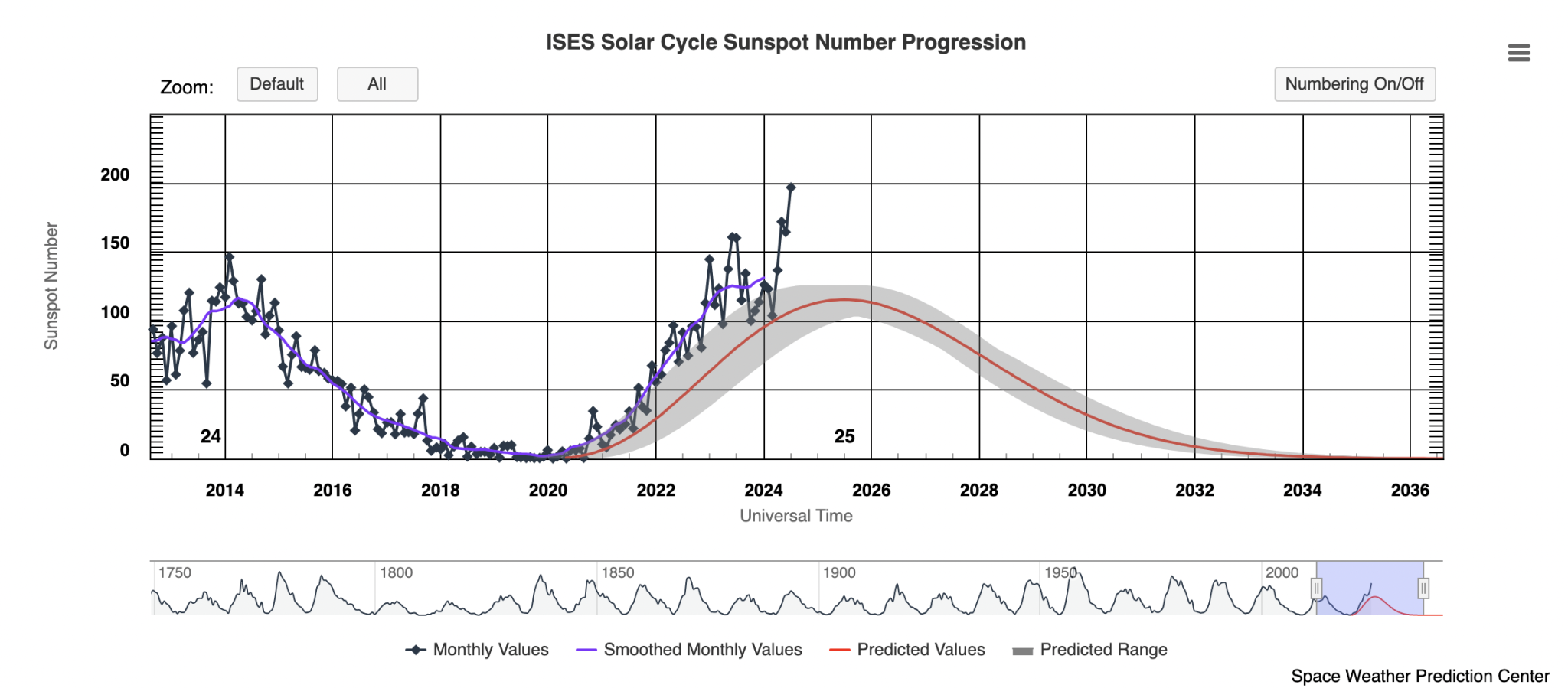
The Latest News for Solar Cycle 25
ADVERTISEMENT
I'm very excited for it to calm down. I always get headaches or get sick.
all very interesting. luckily no matter what, the human kind is not powerful enough to influence the sun to spiff out more or less solar flares and no regulator to adjust the strength. one of those mega explosions over-shooting earth and we get torched. All by chance. Yet some well-paid scientists from the climate change ground hog group suggest we can manage the atmosphere and warning/cooling by increasing /reducing greenhouse farting, monitoring cows and volcanos. i think our human management skills should stick to picking up our trash and not discarding it into the oceans. But besides that, we are pretty much all the stupid human kind incapable of persuading a solar flare to change course let alone “please decrease strength”. I mean Bill Gates wants controllable solar reflective space garbage floating in orbit.
This is not stupidity. The vast majority of grassroots human society is made up of people with very strong sociopath tendencies. They are characterized by people who embrace authoritarianism, censorship, police states, human rights violations etc. These people decide who the political establishment is. They flow up into all the institutions of society. It is why the scientific, medical and educational establishment are corrupt, suppressive and the lap dogs for every major government in the world. The lies of global warming and Covid threat are the norm for our world. There is very little support for truth and humanity among the vast majority of the human population.
Looking at the data most major hurricanes happen during solar min.
There is NO data which supports that.
Thank you for an easily understood explanation.
I wonder if some years we have "open" winters without much snow then in a few years we have snow up to our shoulders,, is result of the sun's cycles???
Nail=Head! You hit it
It seems odd to conclude that the earth should get even warmer as the current solar minimum ends. The fact is that sunspot activity is at a low right now and it would seem the logical conclusion would be a colder winter.
Thomas, you are right about low sunspot activity being associated with cooler temperatures. However, there are other mitigating factors (CO2 is NOT one of them as it isn't a meaningful factor at all). Lower sunspot numbers mean less "solar wind" that disrupts cosmic rays. Cosmic rays are known to "seed" clouds in the atmosphere (provide something for water vapor to condense around forming water droplets which accumulate to clouds). More cloud cover means cooler temperatures. So there is a definite link. However, the atmospheric steering currents (PDO, NAO, etc.) are influenced by ENSO cycles which, in turn, may reflect geologic activity in the western Pacific. We're in a changeable ENSO pattern, so early, mid, and late winter may be mild in one area, cold in others and change during the season. Despite all the baseless thunder from the UN-IPCC, weather and climate are far too complex for any scientist to be able to predict with certainty what the future holds. We can only generalize based on typical circumstances. The same reason weathermen have less than perfect accuracy. So in general, solar minima produce cooler climate whild solar maxima produce warmer climate, but not every year. Hope this helps.